Embracing the Future of Healthcare: The Rise of Telemedicine
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, one innovation stands out for its transformative potential: telemedicine. This approach leverages technology to deliver medical services remotely, breaking down traditional barriers to healthcare access. As we navigate the digital age, telemedicine is becoming a cornerstone of modern healthcare, offering convenience, efficiency, and improved patient outcomes.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine refers to the use of telecommunications technology to provide healthcare services from a distance. This can include video consultations, remote monitoring, and digital transmission of medical information.
By enabling patients to connect with healthcare providers without needing to travel, telemedicine is revolutionizing the way we think about and deliver healthcare.
The Benefits of Telemedicine
Increased Access to Care
Telemedicine eliminates geographical barriers, making it possible for patients in rural or underserved areas to access specialist care that would otherwise be unavailable. This democratization of healthcare ensures that more people receive the medical attention they need, regardless of location.
Convenience and Efficiency
For many, visiting a doctor involves taking time off work, traveling, and waiting. Telemedicine reduces or eliminates these inconveniences. Patients can consult with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, leading to fewer disruptions in their daily lives and more timely medical attention.
Cost-Effectiveness
By reducing the need for physical infrastructure and lowering travel costs, telemedicine can be more cost-effective for both patients and providers. Additionally, it can help mitigate the high costs associated with emergency room visits by providing timely interventions that prevent medical issues from escalating.
Improved Patient Engagement and Outcomes
Telemedicine facilitates better patient engagement through regular follow-ups and easy access to healthcare advice. This continuous care model can lead to improved health outcomes, as patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and manage chronic conditions effectively.
Telemedicine in Action: Real-World Applications
Chronic Disease Management
Patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease benefit significantly from telemedicine. Remote monitoring devices allow for continuous tracking of vital signs, which can be reviewed by healthcare providers in real-time, enabling prompt interventions and personalized care adjustments.
Mental Health Services
Telemedicine has been a game-changer in the mental health sector. Virtual therapy sessions provide a level of anonymity and convenience that can be crucial for those hesitant to seek help. The flexibility of telehealth appointments also means that patients can receive consistent support, which is vital for mental health treatment.
Emergency Care
In emergency situations, telemedicine can expedite the diagnostic process. Remote consultations with specialists can provide critical guidance to on-site healthcare providers, ensuring timely and accurate treatments, especially in cases where specialist availability is limited.
The Future of Telemedicine
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, highlighting its necessity and potential. As we move forward, telemedicine is expected to continue growing, driven by advancements in technology such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and wearable health devices. These innovations will further enhance the capabilities of telemedicine, making it an even more integral part of healthcare.
Telemedicine in the era of COVID
The coronavirus pandemic has changed this, with the number of Medicare patients using telehealth services increasing from roughly 11,000 a week to over 650,000 people a week. This surge in usage has benefitted telemedicine companies like Teladoc and American Well, as well as video conferencing companies like Zoom. Telemedicine visits surged to 50 percent in March and are projected to reach 200 million by the end of 2020.
Despite its benefits, telemedicine is not without challenges. Insurance restrictions, technological requirements, and reluctance from both doctors and patients have all been barriers to its adoption. However, the current health crisis has accelerated its use and may permanently change the way health care is delivered.
Telemedicine doesn't just offer a safer way to provide care during a pandemic; it also has the potential to address chronic issues in the health care system, such as accessibility and cost. However, it is not a panacea. Not all medical issues can be resolved remotely, and there are still significant disparities in internet access, which could exacerbate existing health inequities.
As hospitals and health systems adapt to this new reality, it's clear that telemedicine will be a significant part of the future of health care. Whether it remains a central component post-pandemic will depend on factors such as regulatory changes, patient satisfaction, and the viability of telemedicine as a business model.
It's important to note, however, that while telemedicine has helped maintain some business for the health care industry, visit volumes are still down, and this could hurt the system financially over the long term. Financial assistance from the federal government may not be enough to prevent hospital bankruptcies.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, telemedicine is not without challenges. Ensuring the security and privacy of patient data is paramount, as is addressing the digital divide that may prevent some populations from accessing telehealth services.
Regulatory frameworks also need to evolve to keep pace with the rapid advancements in telemedicine technology.
Despite these challenges, many expect telemedicine to continue to grow. The Cleveland Clinic predicts that within five years, half of the outpatient visits in the U.S. will be virtual. While telemedicine can't replace all in-person care, it offers a more efficient and convenient option for many patients and could help reduce the overall cost of health care.
Using Open-source Messaging Systems as a Telemedicine infrastructure
Nowadays, an open-source messaging system can serve as a powerful infrastructure for efficient communication. This system can bridge the gap between healthcare professionals and patients, ensuring seamless interaction and exchange of crucial medical information.
Open-source messaging systems are cost-effective and customizable, allowing healthcare providers to modify the system to suit their needs. This flexibility can enhance the service delivery of telemedicine, providing a platform that is responsive and adaptable to the changing needs of patients and healthcare professionals.
With features like real-time communication, file sharing, and end-to-end encryption, these systems can support the dynamic nature of telemedicine. They can facilitate immediate consultation, secure transfer of medical records, and ensure the privacy of sensitive patient information.
However, integrating an open-source messaging system into the telemedicine infrastructure comes with its challenges. These include ensuring the system's security, maintaining patient privacy, and navigating potential technical issues. Despite these hurdles, the potential benefits of such a system make it a promising solution for advancing telemedicine.


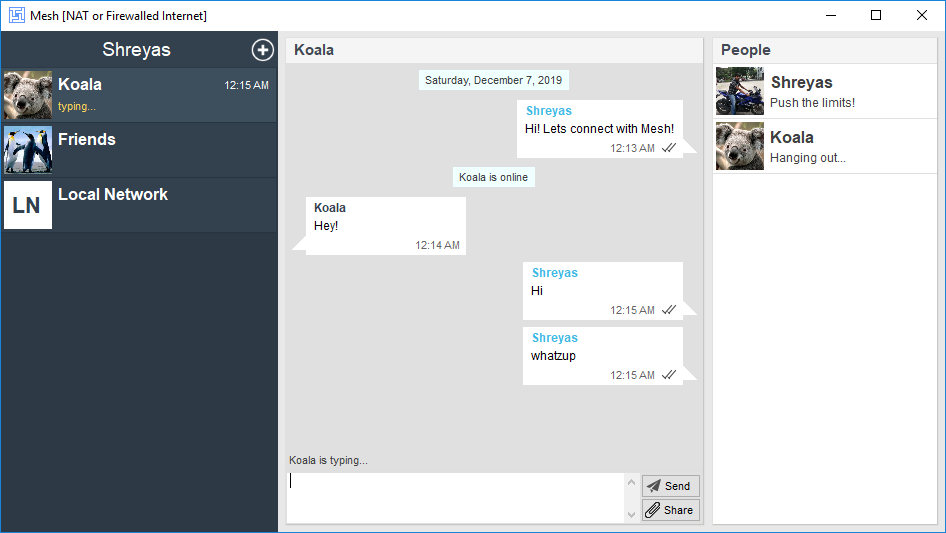

Choose the right Open-source System for your Telemedicine Setup
Conclusion
Telemedicine represents a significant shift in the healthcare paradigm, offering a promising solution to many of the challenges faced by traditional healthcare systems.
By embracing this technology, we can create a more inclusive, efficient, and effective healthcare environment that benefits providers and patients alike. As we continue to innovate and refine telemedicine practices, the future of healthcare looks brighter than ever.