Streamlining Healthcare Operations: Effective Implementation and Key Advantages of a Document Management System
Table of Content
What is a Document Management System?
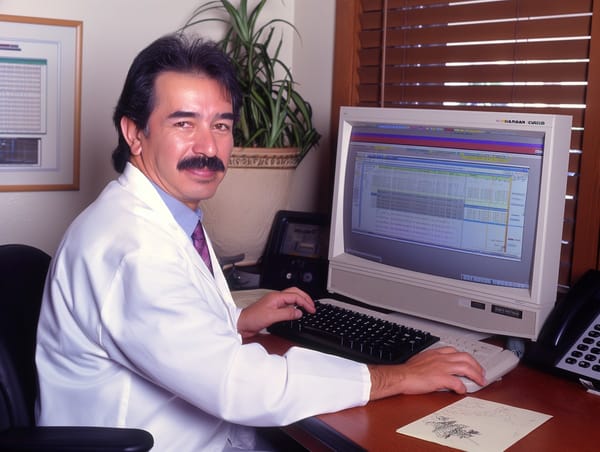
A Document Management System (DMS) is software used to store, manage, and track electronic documents and images of paper documents. It helps in organizing, securing, and retrieving documents efficiently, ensuring that the right information is accessible to the right people at the right time.
Implementing a self-hosted, on-premise DMS empowers clinics and hospitals with robust data management capabilities, enhances security, ensures compliance, and provides greater control and customization, ultimately improving patient care and operational efficiency.
Why Clinics and Hospitals Should Have Their Own Self-Hosted and On-Premise DMS
Enhanced Data Security
Self-hosted DMS ensures that sensitive patient information is stored within the clinic or hospital's infrastructure, reducing the risk of data breaches from external sources.
Control Over Data
Clinics and hospitals have full control over their data, including how it is stored, accessed, and backed up. This autonomy allows for tailored security measures and compliance practices.
Compliance with Regulations
On-premise DMS allows better control over compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, ensuring that all data handling practices meet stringent legal requirements.
Customization
An on-premise solution can be customized to meet the specific needs of the healthcare facility, including unique workflows, security protocols, and user access levels.
Improved Performance
Localized data storage can result in faster access times and better performance, as data retrieval does not depend on internet speed or external servers.
Reliability and Up-time
On-premise DMS can offer greater reliability since it is not subject to the downtimes and outages that can affect cloud-based solutions.
Cost Control
While the initial setup cost may be higher, self-hosted solutions can be more cost-effective in the long run, eliminating recurring subscription fees and potential costs associated with data breaches.
Integration with Existing Systems
On-premise DMS can be more easily integrated with other existing local systems, such as electronic health records (EHR), billing systems, and laboratory information systems (LIS).
Scalability
#Clinics and hospitals can scale their DMS based on their specific needs without relying on the limitations or pricing structures of cloud service providers.
Data Sovereignty
Ensures that data remains within the geographical and jurisdictional boundaries required by law, avoiding issues related to data residency and cross-border data transfers.
Long-Term Data Retention
On-premise solutions provide better options for long-term data retention, archiving, and retrieval, ensuring that historical patient records are always accessible when needed.
Optimizing Healthcare Data Management: Addressing HIPAA and GDPR Compliance with DMS
1. Data Security and Privacy
Securing patient data from unauthorized access and breaches is paramount. Both HIPAA and GDPR impose rigorous requirements for safeguarding data, necessitating robust security measures within Document Management Systems (DMS).
2. Compliance and Documentation
Healthcare providers must meticulously maintain records to demonstrate adherence to regulations. A DMS must facilitate comprehensive compliance tracking and documentation, which can be resource-intensive but essential for meeting regulatory demands.
3. Access Control
Implementing strict access controls is crucial to ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive patient information. At the same time, the DMS must maintain usability for healthcare staff, balancing security with operational efficiency.
4. Data Subject Rights
GDPR grants patients rights to access, rectify, and erase their data. A DMS must efficiently manage these requests while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, presenting a significant operational challenge.
5. Cross-Border Data Transfers
GDPR restricts the transfer of personal data outside the EU, complicating the management of international operations. Healthcare providers using a DMS must navigate these complex regulations to ensure data transfer compliance.
6. Audit and Monitoring
Ongoing audits and continuous monitoring are required to ensure compliance with both HIPAA and GDPR. A well-designed DMS should support regular audits and real-time monitoring to reduce the administrative burden and maintain adherence to regulatory standards.
Addressing these challenges through a well-implemented DMS can enhance the efficiency and security of healthcare operations, contributing to better patient outcomes and robust regulatory compliance.
DMS for Healthcare