How to Upload files to a Directory with Flask and Python?
Are You Truly Ready to Put Your Mobile or Web App to the Test?
Don`t just assume your app works—ensure it`s flawless, secure, and user-friendly with expert testing. 🚀
Why Third-Party Testing is Essential for Your Application and Website?We are ready to test, evaluate and report your app, ERP system, or customer/ patients workflow
With a detailed report about all findings
Contact us nowTable of Content
In this tutorial, we will explore how to upload files to a directory using Flask, a popular Python web framework. Flask provides a lightweight and flexible way to handle file uploads, allowing you to build web applications that accept and store user-submitted files.
We will walk through the step-by-step process of creating a Flask application that includes a file upload feature. You will learn how to set up the necessary routes, handle file uploads, and save the uploaded files to a specific directory on your server.
If you are a beginner, this tutorial will provide you with the knowledge and skills to implement file uploading functionality in your Flask applications. So let's get started and learn how to upload files to a directory with pure Flask!
1- Setup Flask!
To set up Flask using pip, follow these steps:
- Open your command-line interface (such as Terminal or Command Prompt).
- Make sure you have Python and pip installed on your system.
- Wait for the installation to finish. Flask and its dependencies will be downloaded and installed.
- Once the installation is complete, you can start using Flask to develop web applications.
Run the following command to install Flask:
pip install flask
Note: It's recommended to set up a virtual environment before installing Flask to keep your project dependencies isolated. You can use tools like virtualenv or venv to create a virtual environment.
2- Create your App file
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
return 'Hello, World!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
3- Create the Upload Form Template
Create your upload form in ./templates/index.html.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>FLASK File Uploads</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Upload your file</h1>
<form method="POST" action="" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<p><input type="file" name="file"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="Submit"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>4- Perform the File Upload Action
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, url_for
import os
from os.path import join, dirname, realpath
app = Flask(__name__)
# enable debugging mode
app.config["DEBUG"] = True
# Upload folder
UPLOAD_FOLDER = 'files'
app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'] = UPLOAD_FOLDER
# Root URL
@app.route('/')
def index():
# Set The upload HTML template '\templates\index.html'
return render_template('index.html')
# Get the uploaded files
@app.route("/", methods=['POST'])
def uploadFiles():
# get the uploaded file
uploaded_file = request.files['file']
if uploaded_file.filename != '':
file_path = os.path.join(app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], uploaded_file.filename)
# set the file path
uploaded_file.save(file_path)
# save the file
return redirect(url_for('index'))
if (__name__ == "__main__"):
app.run(port = 5000)5- List the uploaded files in the upload Directory
To list the uploaded files from the upload directory, we will edit our main Root Route function:
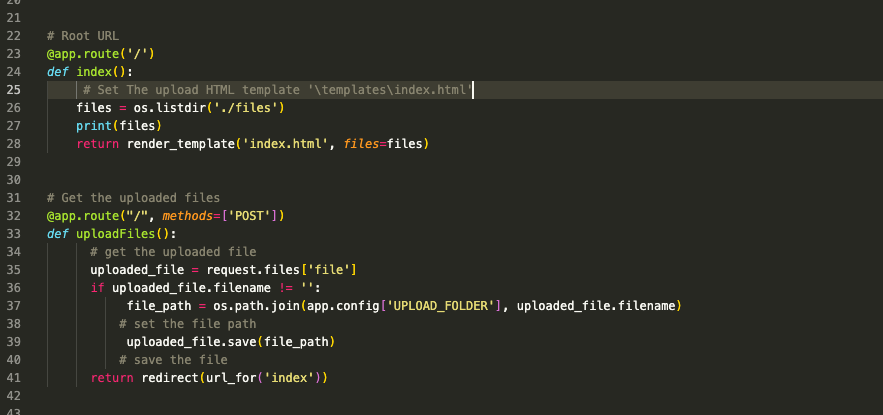
# Root URL
@app.route('/')
def index():
files = os.listdir('./files')
return render_template('index.html', files=files)Then we will display the files in the HTML template:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>FLASK File Uploads</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Upload your file</h1>
<form method="POST" action="" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<p><input type="file" name="file"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="Submit"></p>
</form>
<!--uploded files-->
<div>
<ul>
{% for file in files %}
<li>{{ file }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
<!--/uploded files-->
</body>
</html>6- Bonus: Access from the local network
If you want to access your Flask development server and test your app within your local network, edit your host setting:
if __name__ == '__main__':
# run app in debug mode on port 5000
app.run(debug=True, port=5055, host='0.0.0.0')Now you know how to perform simple file uploads using Flask.