VictoriaMetrics: Self-hosted Monitoring Solution and Time Series Database
Table of Content
VictoriaMetrics is a fast, cost-effective, and scalable monitoring solution and time series database. It can be used as long-term storage for Prometheus, a drop-in replacement for Prometheus and Graphite in Grafana, and offers easy setup and operation. VictoriaMetrics has achieved security certifications and implements MetricsQL, an improved query language.
VictoriaMetrics is available in binary releases, Docker images, Snap packages and source code.

Supported Metrics
VictoriaMetrics has the following prominent features:
- It can be used as long-term storage for Prometheus. See these docs for details.
- It can be used as a drop-in replacement for Prometheus in Grafana, because it supports Prometheus querying API.
- It can be used as a drop-in replacement for Graphite in Grafana, because it supports Graphite API. VictoriaMetrics allows reducing infrastructure costs by more than 10x comparing to Graphite - see this case study.
- It is easy to setup and operate:
- VictoriaMetrics consists of a single small executable without external dependencies.
- All the configuration is done via explicit command-line flags with reasonable defaults.
- All the data is stored in a single directory pointed by
-storageDataPatha command-line flag. - Easy and fast backups from instant snapshots can be done with vmbackup / vmrestore tools. See this article for more details.
- It implements PromQL-like query language - MetricsQL, which provides improved functionality on top of PromQL.
- It provides global query view. Multiple Prometheus instances or any other data sources may ingest data into VictoriaMetrics. Later this data may be queried via a single query.
- It provides high performance and good vertical and horizontal scalability for both data ingestion and data querying. It outperforms InfluxDB and TimescaleDB by up to 20x.
- It uses 10x less RAM than InfluxDB and up to 7x less RAM than Prometheus, Thanos or Cortex when dealing with millions of unique time series (aka high cardinality).
- It is optimized for time series with high churn rate.
- It provides high data compression, so up to 70x more data points may be stored into limited storage comparing to TimescaleDB according to these benchmarks and up to 7x less storage space is required compared to Prometheus, Thanos or Cortex according to this benchmark.
- It is optimized for storage with high-latency IO and low IOPS (HDD and network storage in AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, etc). See disk IO graphs from these benchmarks.
- A single-node VictoriaMetrics may substitute moderately sized clusters built with competing solutions such as Thanos, M3DB, Cortex, InfluxDB or TimescaleDB. See vertical scalability benchmarks, comparing Thanos to VictoriaMetrics cluster and Remote Write Storage Wars talk from PromCon 2019.
- It protects the storage from data corruption on unclean shutdown (i.e. OOM, hardware reset or
kill -9) thanks to the storage architecture. - It supports powerful stream aggregation, which can be used as a statsd alternative.
- It supports metrics relabeling.
- It can deal with high cardinality issues and high churn rate issues via series limiter.
- It ideally works with big amounts of time series data from APM, Kubernetes, IoT sensors, connected cars, industrial telemetry, financial data and various Enterprise workloads.
- It has open source cluster version.
- It can store data on NFS-based storages such as Amazon EFS and Google Filestore.
UI
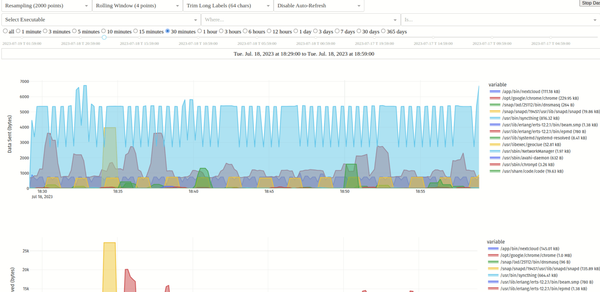
VictoriaMetrics provides UI for query troubleshooting and exploration. The UI is available at http://victoriametrics:8428/vmui. The UI allows exploring query results via graphs and tables. It also provides the following features:
- Explore:
- Metrics explorer - automatically builds graphs for selected metrics;
- Cardinality explorer - stats about existing metrics in TSDB;
- Top queries - shows most frequently executed queries;
- Active queries - shows currently executed queries;
- Tools:
- Trace analyzer - playground for loading query traces in JSON format;
- WITH expressions playground - test how WITH expressions work;
- Metric relabel debugger - playground for relabeling configs.
VMUI automatically switches from graph view to heatmap view when the query returns histogram buckets (both Prometheus histograms and VictoriaMetrics histograms are supported). Try, for example, this query.
Graphs in vmui support scrolling and zooming:
- Select the needed time range on the graph in order to zoom in into the selected time range. Hold
ctrl(orcmdon macOS) and scroll down in order to zoom out. - Hold
ctrl(orcmdon macOS) and scroll up in order to zoom in the area under cursor. - Hold
ctrl(orcmdon macOS) and drag the graph to the left / right in order to move the displayed time range into the future / past.
Query history can be navigated by holding Ctrl (or Cmd on macOS) and pressing up or down arrows on the keyboard while the cursor is located in the query input field.
License
- Apache 2.0 License
Resources