10 Use Cases of IAM (Identity and Access Management) Solutions
IAM, short for Identity and Access Management, is a framework that helps organizations manage and secure digital identities. It is a set of policies, procedures, and technologies used to manage identities and control access to resources within an organization.
An Identity Access Management system is responsible for managing user authentication, authorization, and access control in an organization. It enables organizations to ensure that users can access the resources they need to do their jobs while also ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive or confidential data.
Why is IAM important for enterprise?
IAM is crucial for enterprise security because it helps organizations control access to their sensitive data and systems. With IAM, organizations can ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data, which reduces the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Moreover, it helps to streamline user management and provides a single point of control for all user-related activities.
10 Use-cases of IAM Identity And Access Management System
1- Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a process that enables users to access multiple applications with a single set of login credentials. With SSO, users don't have to remember multiple usernames and passwords for different applications, which makes their lives easier. SSO also helps organizations to streamline their authentication processes, reduce IT costs, and improve security.
The way SSO works is by creating a trusted relationship between the Identity Provider (IDP) and the Service Provider (SP). When a user tries to access a protected resource on the SP, the SP redirects the user to the IDP, which authenticates the user and returns a security token to the SP.
The token contains information about the user and the authentication event, which the SP uses to grant the user access to the protected resource. SSO has become an essential tool for many organizations that use cloud-based applications, as it simplifies the management of user access control and reduces the risk of security breaches.
2- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires multiple forms of identification to access an account. The purpose of MFA is to increase the security of your account by adding extra layers of protection.
Instead of relying solely on a password, MFA requires additional information, such as a fingerprint, a code sent to your phone, or a security token. This ensures that even if your password is compromised, an attacker would still need access to your additional forms of identification in order to gain access to your account.
With the growing number of cyberattacks and data breaches, MFA has become an essential tool in protecting sensitive information and ensuring that only authorized users have access to important accounts.
3- User provisioning and onboarding
User provisioning and onboarding is the process of providing a new user with the necessary tools and resources to access and use a company's systems and applications. This process includes creating user accounts, granting permissions, assigning roles, and providing necessary training and support to ensure a smooth transition into the company's environment.
Additionally, onboarding can also involve introducing new hires to the company culture and values, establishing goals and expectations, and fostering relationships with other employees. Effective user provisioning and onboarding can lead to increased productivity, reduced turnover, and a positive impact on overall company performance.
4- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security model that restricts system access to authorized users. RBAC can be used to manage user rights and permissions, ensuring that users only have access to the resources they need to fulfill their roles. This model is based on the idea that access to system resources should be based on the role that a user plays in the organization.
By assigning roles to users, RBAC makes it easier to maintain a secure system. RBAC is widely used in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and government, to ensure that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access. With RBAC, organizations can improve their security posture by reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
In addition, RBAC can simplify the process of managing user access, making it easier to grant and revoke user permissions as needed to support business needs.
5- Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a critical component of any organization's security strategy. It is designed to identify, track, and manage privileged accounts and activities across the entire IT infrastructure. PAM solutions enable organizations to implement a least privilege approach to access, where users are granted only the necessary access to perform their job functions.
By implementing PAM solutions, organizations can ensure that privileged accounts are secured and monitored at all times, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks. With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, it is essential for organizations to have robust PAM solutions in place to protect their critical assets and maintain business continuity.
6- Identity Governance and Administration (IGA)
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) refers to the policies, procedures, and technologies used to manage digital identities and their access to resources within an organization. It involves the process of identifying individuals in a system and assigning them appropriate access privileges based on their job responsibilities and the principle of least privilege.
IGA solutions are designed to provide a centralized, automated approach to managing user access across an organization's network, systems, and applications. This includes the ability to create, modify, and delete user accounts, as well as manage access to sensitive data and applications.
Effective IGA can help organizations to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, minimize the risk of security breaches, and reduce the time and resources required to manage user access. It also enables organizations to streamline user access requests and approvals, reducing the burden on IT staff and improving overall operational efficiency.
In today's fast-paced business environment, IGA is becoming increasingly important for organizations of all sizes. With the growing number of digital identities and the increasing complexity of enterprise networks, effective IGA is essential for maintaining security and ensuring compliance.
7- Enterprise password management
Enterprise password management is a critical aspect of any organization's cybersecurity strategy. It involves the implementation of policies, procedures, and tools to ensure the secure storage, retrieval, and use of passwords across the enterprise.
One important component of enterprise password management is password complexity. Passwords should be complex enough to resist brute-force attacks, but also easy enough for employees to remember. Organizations can implement password complexity requirements, such as mandating the use of special characters and enforcing minimum length requirements, to ensure that passwords are sufficiently complex.
Another important aspect of enterprise password management is password rotation. Regularly changing passwords can help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Organizations can implement policies that require employees to change passwords on a regular basis, or that automatically prompt employees to change passwords after a certain period of time.
In addition to these technical measures, organizations should also provide training and education to employees on best practices for password management. This can include tips on creating strong passwords, avoiding common password mistakes, and recognizing phishing attempts that may compromise password security.
Overall, enterprise password management is a complex and multifaceted process that requires a combination of technical measures and employee education to ensure the security of sensitive information. By implementing effective password management policies and procedures, organizations can help protect themselves against the growing threat of cyber attacks.
8- Access Request Management
Access Request Management is a crucial process that allows organizations to systematically manage and monitor requests for access to sensitive information or resources. By implementing a robust Access Request Management system, organizations can ensure that only authorized personnel are granted access to sensitive information, thereby minimizing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized use of resources.
To establish an effective Access Request Management process, organizations must first assess their needs and identify the key stakeholders involved in the process. This may include IT personnel, security teams, and business units that require access to sensitive information. Once the key stakeholders are identified, organizations can establish policies and procedures for requesting, approving, and monitoring access requests.
In addition to implementing policies and procedures, Access Request Management systems may also include features such as automated workflows, audit trails, and reporting capabilities. These features can help organizations streamline the access request process, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards.
Access Request Management is a critical component of any organization's security and risk management strategy. By implementing a comprehensive Access Request Management system, organizations can better protect their sensitive information and resources, and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
9- Data and Access Federation
Federation is a concept that involves multiple organizations working together to achieve a common goal. In terms of Identity Federation, this means that different organizations can allow their users to access resources and services from other organizations using the same set of credentials.
This allows for a more seamless user experience, as users do not need to remember multiple sets of credentials for different services. Additionally, it can also improve security by allowing for centralized authentication and access control. One example of Identity Federation in action is the use of Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions, which allow users to log in once and access multiple services without needing to re-authenticate each time.
10- Auditing
The process of audit and compliance reporting is crucial for any organization as it helps in the identification of potential risks and threats to the company's operations. It involves a thorough review of the company's financial records, internal controls, and compliance with regulations and laws. The audit and compliance reporting process is not only essential for identifying risks, but also for ensuring that the company is following ethical and legal practices.
In addition, it plays a key role in building trust and credibility with stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees. Therefore, it is important for organizations to have an effective audit and compliance reporting framework in place that includes regular monitoring, reporting, and remediation of any issues that may arise. Overall, the audit and compliance reporting process serves as a critical tool in ensuring the long-term success and sustainability of an organization.
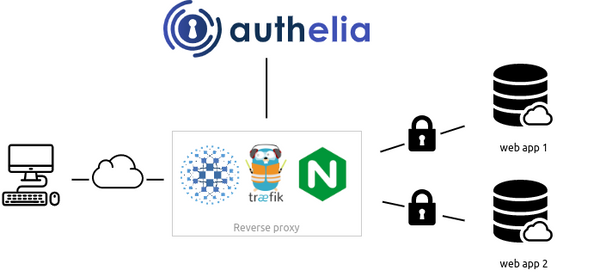
Benefits of using Open-source IAM
Open-source IAM solutions are becoming increasingly popular as more organizations look for cost-effective ways to manage their digital identities. The benefits of using open-source IAM include:
- Lower costs: Open-source IAM solutions are often free to use, which can significantly reduce the cost of implementing an IAM solution.
- Flexibility: Open-source IAM solutions are highly customizable, enabling organizations to tailor the solution to their specific needs.
- Community support: Open-source IAM solutions have a large community of developers and users who can provide support and guidance.
- Security: Open-source IAM solutions are typically more secure than proprietary solutions, as they are subject to constant scrutiny from the community.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IAM is an essential component of any organization's security strategy, and it provides numerous benefits, including streamlined user management, improved security, and reduced costs. By leveraging open-source IAM solutions, organizations can achieve these benefits at a lower cost while also maintaining flexibility and community support.