IoT in Healthcare: what’s new and what’s next?
Table of Content
IoT in Healthcare: what’s new and what’s next?
There’s going to be a projected 12% annual increase in the number of devices connected to the internet of things annually. This increase will see these gadgets increase to 125 billion by the year 2030 from the recorded estimate of 27 billion in the year 2017.
This revolution has changed and to a notable extent improved how things are done in many sectors. The result is that there has been an increase in the gains realized from many ventures. The health sector is one of the sectors that have reaped benefits from the IoT technology.
An Overview of How the IoT Is Used In Healthcare
In matters of healthcare, the internet of things has opened up many opportunities and possibilities. Many smart devices are being interconnected and put to use by both the patients and the health practitioners all in a bid to transform the healthcare sector.
The devices are configured in a system that allows them to capture and transmit data through an internet connection. Users are advised to do this over internet connections that will not compromise their data security. This is made possible through the use of real-time monitors, sensors, cameras, and actuators among other sophisticated devices.
Once integrated to work together, the devices can bring and deliver the expected health reports. The sensors and other monitors receive data in analogue form after which this information is digitized, processed and moved to the data cloud. It's then sent to the intended recipient who can take the required action.
This digitization quickens consultations and saves a good fraction of the time and money that patients would have otherwise spent on visiting a health care facility in person. The result is an improved health care system, better treatment outcomes and great workflow.
Challenges Faced While Using IoT in Healthcare
The introduction of IoT in healthcare has not come without its share of challenges. As already discussed above, the system requires the regular transmission of data via the internet.
Medical information is sensitive and should be treated as private and confidential. However, the internet is full of many criminals who would do anything just to comprise data security. Implementing reliable security measures is therefore very pivotal.
Unfortunately, many of the devices that are being used for IoT in healthcare are not encrypted. Others are running on operating systems that are outdated putting the health data at risk.
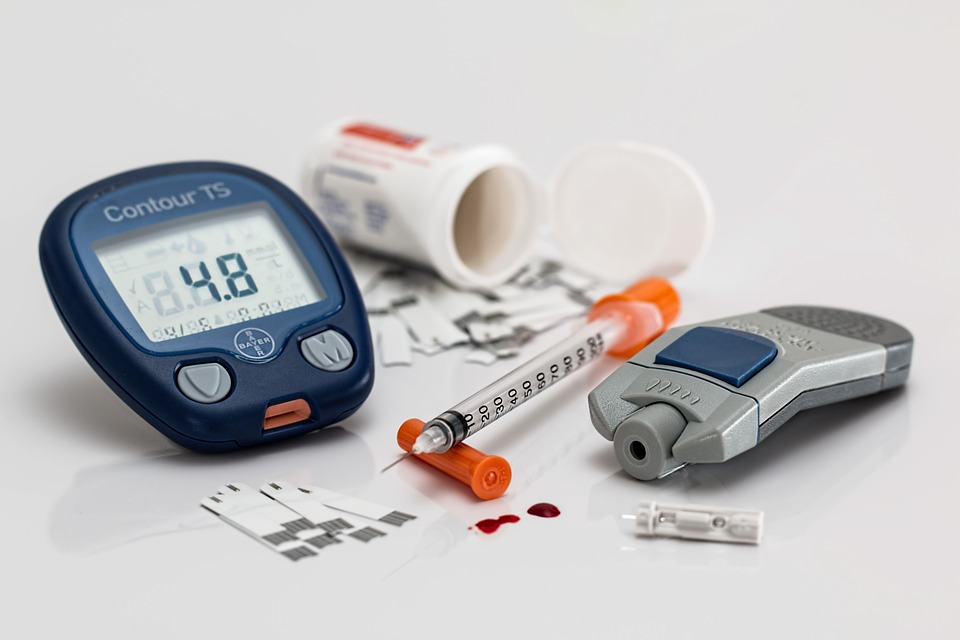
In an experiment that was conducted by researchers in 2018, security researchers were able to easily stop an implantable insulin pump. They were able to completely stop the system from delivering the medication as it was required. This was an indicator of how most of these devices are vulnerable.
Another research indicated that hackers can easily manipulate the pacemaker in a simulator. The researchers were able to hack the system and either speed up or slow down the heart rate. The researchers also reported that they could even shock the defibrillator. Such actions can cause untold harm to patients. Below is a rundown of the things you can do to secure your device.
Install a VPN
Keep your medical device safe by installing a VPN. VPNs secure information by encrypting it so that it reaches the intended recipient without being compromised. When connected on a router, the VPN ensures that all the data on all devices such as vital monitors, smartphones, sensors, and pacemakers connected to that network is safe and secure as long as they are connected within that network.
In addition to getting a VPN connection, it is important to always ensure five golden rules of safe internet use which are:
Setting Up the Device's Passwords.
Some gadgets have default passwords such as ‘0000’ or ‘admin’; others require you to set up passwords. Whenever you are using a healthcare IoT device, set the passwords to something new and that’s only known by you.
Say No Automatic Connections.
It’s very tempting to take advantage of ‘free WI-FI’ without taking any caution of the associated dangers. To avoid the risk of having your IoT medical device automatically connect to new networks, it’s advisable to check your internet settings and disable automatic connections. If need be, be sure about the safety of your data before establishing any new connection to a network.
Update The Device’s Software, Regularly.
This can be annoying but it is an important way of patching up any security vulnerabilities with the current software on your IoT device.
You also need to be careful about where you are plugging in your devices. What might look like a simple plugin might be an avenue for hackers to steal your information.
Conclusion
With the necessary security measures in place, IoT devices can go a long way in improving the quality of healthcare services across the world. When considering the adoption of this technology, all users of IoT in healthcare should be armed with proper security. With this, the health sector will be able to seamlessly benefit from IoT and offer a wide range of benefits to all users.
Brad Smith is a technology expert at TurnOnVPN, a non-profit promoting a safe, secure, and censor-free internet. He writes about his dream for a free internet and unravels the horror behind big techs.