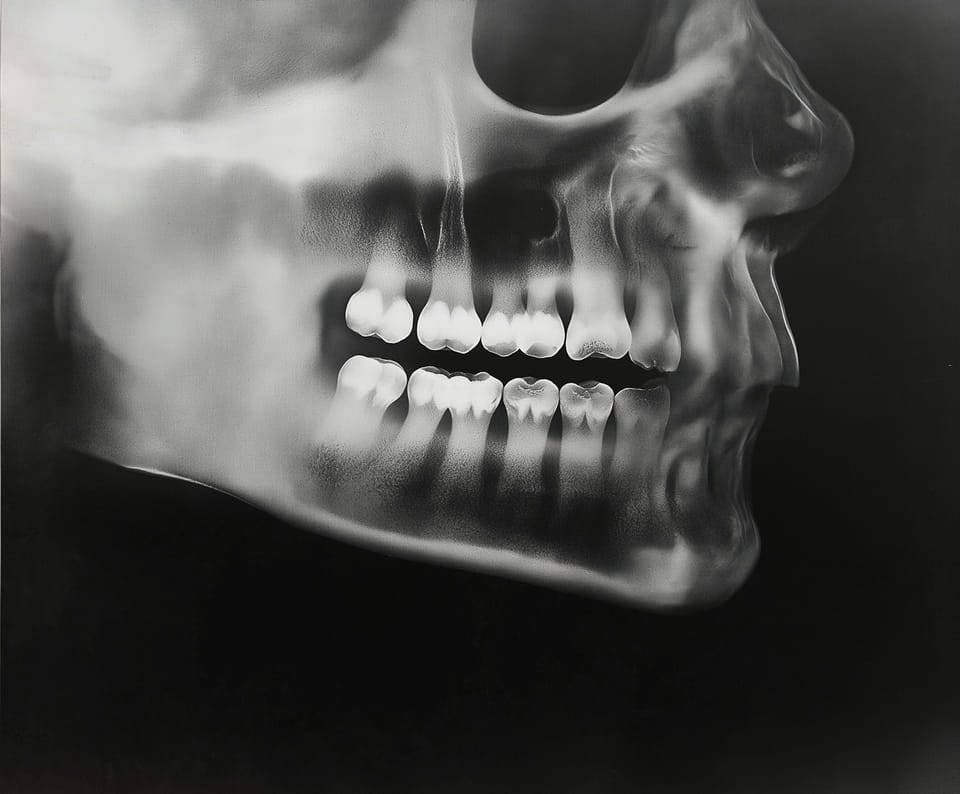
"Open-source Radiology Apps Are a Joke," Says a Radiologist! I Say They are NOT!
Why Open-Source Radiology Software Deserves a Place in Clinics
Table of Content
Recently, I found myself in a heated discussion with a radiologist who dismissed open-source software for radiology. He argued, quite adamantly, that radiology should rely solely on "first-class" proprietary code and equipment, not what he called "community or charity work of online developers." His stance stemmed from a disappointing experience he had years ago with open-source DICOM viewers.
While I respect his opinion, I couldn’t help but feel that it’s based on outdated information and a limited perspective.
As a doctor and software developer, I’ve spent years exploring and using open-source healthcare tools, including radiology software. On Medevel.com, we’ve reviewed over 100 open-source DICOM viewers, PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), and related tools.
Many of these solutions are actively powering clinics, hospitals, and radiology departments across the globe.
Contrary to the belief that these tools are stuck in the past, I’ve seen firsthand how open-source radiology software has evolved to address real-world problems that commercial solutions often overlook.
Addressing Real Needs in Radiology
The radiology field is demanding accuracy, efficiency, and reliability are non-negotiable. While proprietary solutions dominate the market, they often come with limitations like high costs, vendor lock-in, and inflexible update cycles.
Open-source alternatives, such as Orthanc, Horos, OsiriX, 3D Slicer, and Miele-LXIV, were born out of a need to overcome these barriers. These tools have grown thanks to their active communities and the involvement of healthcare professionals who understand the field’s unique challenges.
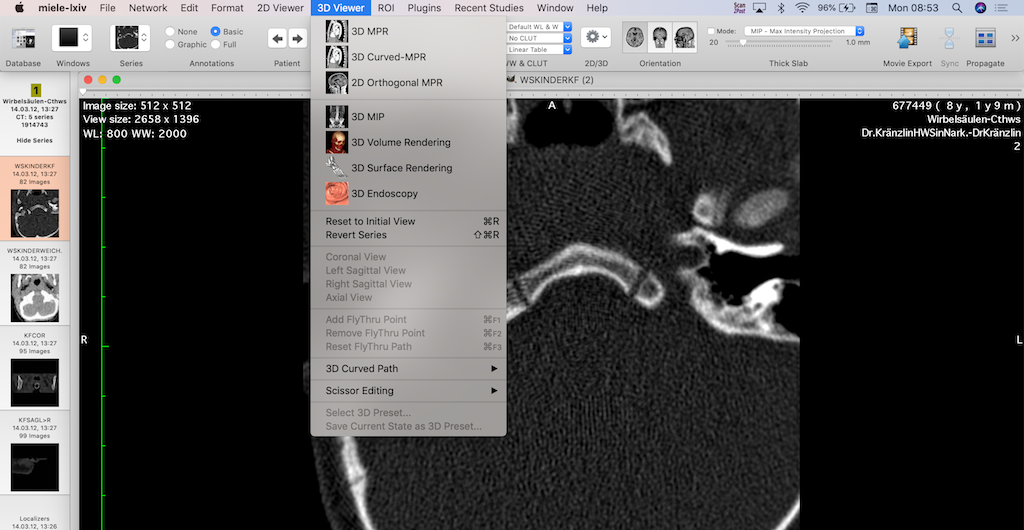
Take Horos and Miele-LXIV for instance. Both are robust DICOM viewers tailored for macOS users. Horos, in particular, has gained significant traction among radiologists, researchers, and educators for its user-friendly interface and customization options.
Similarly, Orthanc stands out for its flexibility and powerful API, making it an excellent choice for hospitals looking to integrate radiology with broader healthcare IT systems.
Bridging the Gap Between Commercial and Open-Source Tools
The argument that open-source lacks the polish or usability of commercial tools is, in many cases, outdated. While it’s true that setting up open-source systems often requires more effort—a DIY approach or professional assistance—the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial investment.
With open-source, you avoid vendor lock-in, inflated costs, and the frustration of waiting years for updates that may never materialize.
Moreover, open-source solutions often fill gaps that commercial tools miss. For instance, portable DICOM viewers like those listed in our detailed review cater to radiologists who need to review scans on the go.
These tools aren’t just functional; they’re indispensable for professionals working in resource-limited settings or remote locations.
The Open-Source Evolution
One of the most common criticisms of open-source healthcare software is the perceived lack of innovation over the past decade. This couldn’t be further from the truth. As I discussed in this article, many open-source projects are thriving, thanks to active developer communities and contributions from healthcare professionals.
For example, 3D Slicer continues to push boundaries in medical imaging, offering advanced features for segmentation, visualization, and analysis.
Additionally, as healthcare infrastructure increasingly embraces Linux and open-source technologies, the integration of radiology software into broader systems has become more seamless.
This trend not only highlights the adaptability of open-source tools but also underscores their growing relevance in modern healthcare.
Recommendations for Clinics Considering Open-Source Radiology Software
If you’re a clinic or hospital looking to incorporate open-source radiology software, here are some tips to ensure a smooth transition:
- Start Small: Begin with a specific use case, such as a DICOM viewer like Horos or Miele-LXIV, to assess compatibility and usability.
- Engage Professionals: While open-source offers freedom, setting up and maintaining these systems often requires expertise. Consider hiring professionals familiar with the tools you plan to use.
- Leverage the Community: The open-source community is one of your greatest assets. Participate in forums, contribute to discussions, and seek advice from other users.
- Invest in Training: Ensure your staff understands how to use the software effectively. Many open-source projects offer detailed documentation and tutorials.
- Focus on Integration: Tools like Orthanc are highly customizable and can integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare IT systems. Plan your integration strategy to maximize efficiency.
Final Words
Open-source radiology software is not a second-rate alternative to proprietary systems; it’s a viable, often superior option for clinics and hospitals willing to invest the time and effort.
By embracing open-source, healthcare providers can benefit from greater flexibility, cost savings, and the ability to adapt quickly to changing needs. The days of dismissing open-source as "charity work" are long gone—it’s time we give these tools the recognition they deserve.