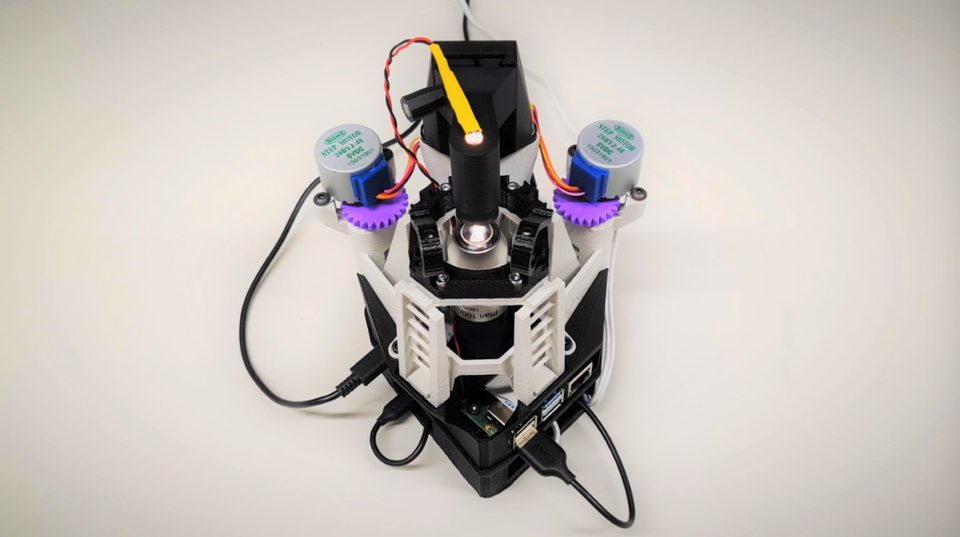
OpenFlexure is an Open-source 3D-Printed Low-cost Microscope
The OpenFlexure Microscope is a 3D printable microscope, including a precise mechanical stage to move the sample and focus the optics. There are many different options for the optics, ranging from a webcam lens to a 100x, oil immersion objective.
It comes with a sophisticated guide that helps anyone print the microscope with any 3D printer, an open-source software to start using the microscope which works on Windows, Linux, and macOS, and rich tutorials to make its usage smooth and fun.
Optomechanics is a crucial part of any microscope; when working at high magnification, it is absolutely crucial to keep the sample steady and to be able to bring it into focus precisely.
Accurate motion control is extremely difficult using printed mechanical parts, as good linear motion typically requires tight tolerances and a smooth surface finish.
This design for a 3D printed microscope stage uses plastic flexures, meaning its motion is free from friction and vibration. It achieves steps well below 100 nanometers when driven with miniature stepper motors, and is stable to within a few microns over several days.
Key features
- High performance
- Low-cost
- Highly customizable
- Ready for lab works
Resources